to mathematical models is often costly
Great Lakes Human Health
experimental work that can take months to years
Effects Research Program
to complete.
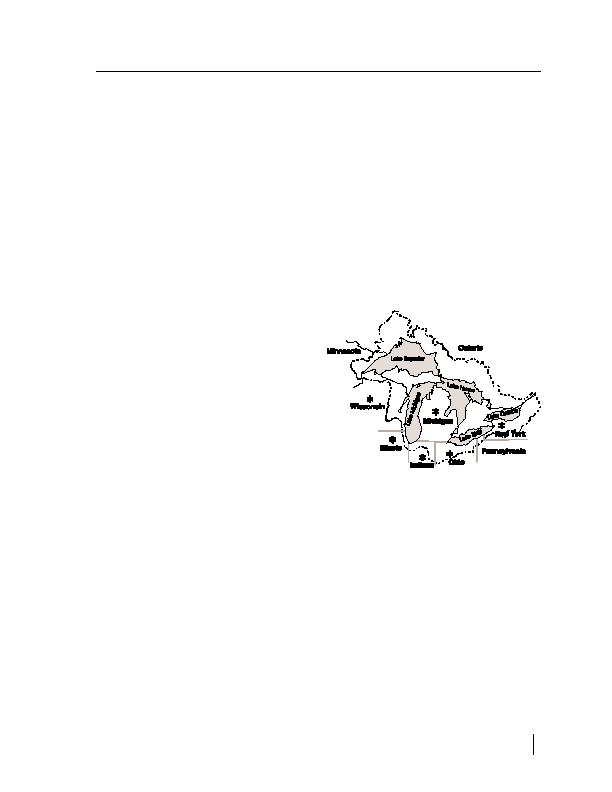
The Great Lakes Human Health Effects Re-
The computational toxicology laboratory has
search Program is intended to build on, and
been used to provide critical toxicological
amplify, the results of past and ongoing fish-
information that supports agencywide programs
consumption research in the Great Lakes basin,
and activities. Following are highlights of some
using existing structures and institutions already
of the major projects and activities conducted
involved in human health research. This
during fiscal year 2000.
ATSDR-supported research program studies
known at-risk populations to further define the
New minimum risk levels (MRLs) for
human health consequences of exposure to
methylene chloride were derived by develop-
ing and using a PBPK model.
Great Lakes basin.
derived by applying BMD modeling technol-
ogy to the data set.
A pharmacokinetic model for aluminum was
developed that provided convincing evidence
that using aluminum compounds in childhood
vaccines is safe. Both CDC and the World
Health Organization used the ATSDR assess-
ment to recommend continued use of alumi-
num in childhood vaccines. Aluminum is
used in certain vaccines to increase immuno-
logic response and thus make the vaccine
more effective.
Development of safe fish consumption levels
During fiscal year 2000, significant research
for women and children who eat fish contain-
ing dioxins.
the following.
SAR analyses of a styrene-acrylonitrile trimer
The relationship between prenatal exposure to
were critical in a multiagency decision to
PCBs and performance on the Fagan Test of
pursue reproductive toxicology testing of this
compound found in the drinking water in
infants at 6 months and again at 12 months.
Toms River, New Jersey.
The results indicated a significant relationship
Development and utilization of a PBPK
between exposure to PCBs and poor perfor-
model for PCBs to determine route-specific
mance on the FTII. No significant relation-
sources contributing to high serum PCB
ship was found between exposure to DDE or
levels in Anniston, Alabama. The model
methyl mercury on any tests of the FTII.
simulations indicated that high PCB soil
PCBs and DDE were markedly elevated in a
levels were an important exposure route.
cohort of adults who consumed fish. Expo-
sure to PCBs, but not to DDE, was associated
with lower scores on several measures of
memory and learning.
chapter 2 37



 Previous Page
Previous Page
